Hire experienced
software engineers
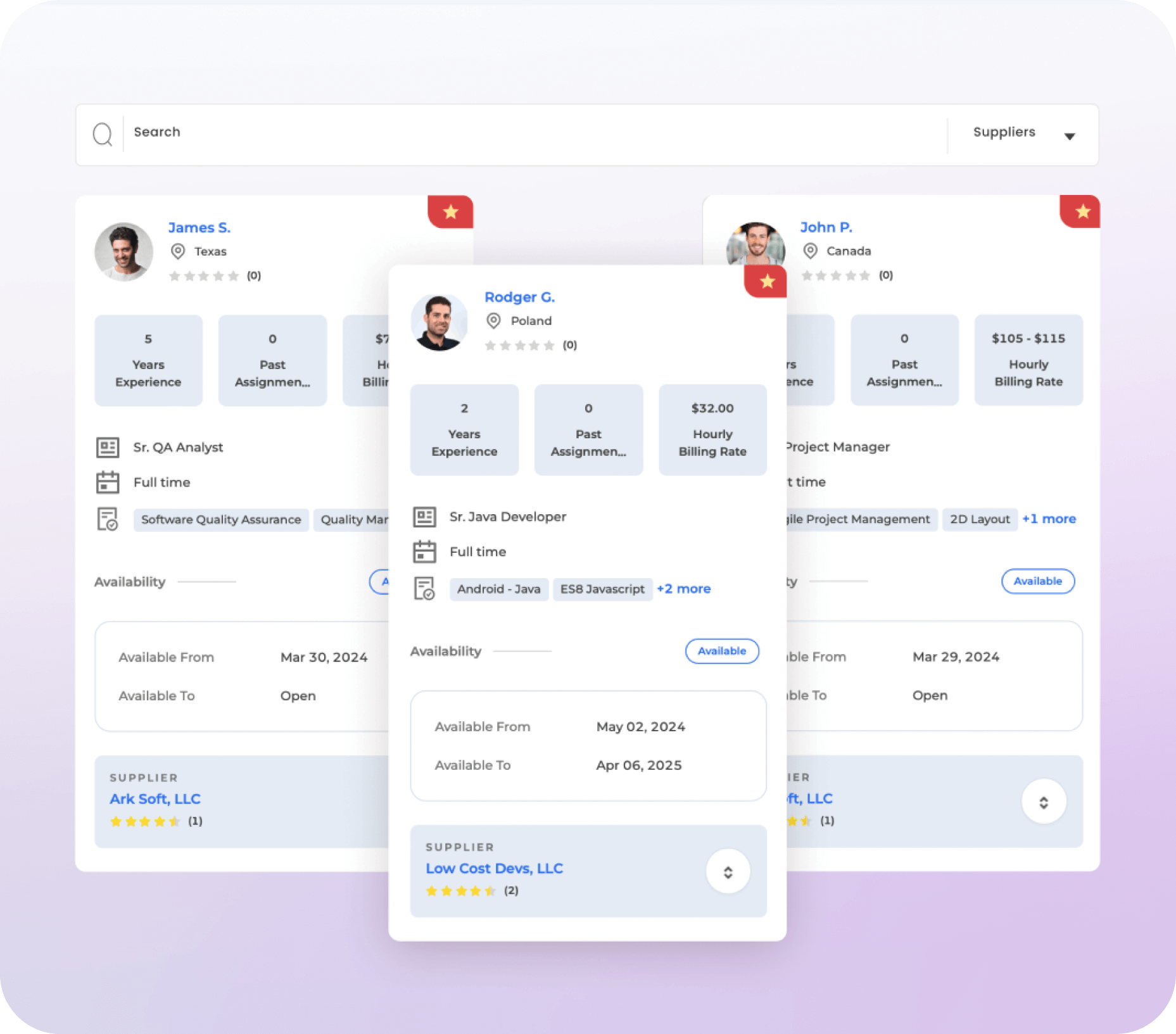
Need help filling
your software engineering roles?
Accelerate your product delivery and close your project’s engineering skill gaps
quickly, efficiently and affordably by working with our incredible talent partners.
Full-time hires
Receive perfectly matched software engineer candidates in record time by engaging with hundreds of local recruiting firms on our platform ready to take on your hard-to-fill software engineer roles.
Temporary resources
Hire a software engineer or build a whole team of software engineers by working with hundreds of staffing agencies and talent vendors dedicated to finding the best talent for your business needs.
Find better talent at lower cost
Reduce billing rates
Lower your contract resource
billing rates by up to
40%
Optimize hiring time
Speed up hiring timelines for
your open roles by up to
30%
Increase candidate flow
Increase number of candidates for your open roles by up to
50%
Reduce talent acquisition costs
Reduce your talent
acquisition costs by up to
30%
Find better talent at lower cost
Reduce billing
rates
Lower your contract resource billing rates by
40%
Reduce talent acquisition costs
Reduce your average talent acquisition costs by
30%
Optimize
hiring time
Speed up hiring timelines for
your open roles by up to
30%
Increase candidate flow
Increase number of candidates for your open roles by up to
50%
Leverage our innovative hiring process
Post your open roles
Share your exact search requirements and connect with top-notch agencies that specialize in your role and industry.
Receive matching profiles
Get well-matched profiles of suitable candidates from multiple vendors for your evaluation and review.
Choose best candidate
Interview and select the best candidate for the job, while receiving continuous support from agency recruiters.
Hire and onboard
Onboard your new hire onto your project team within days of posting your open vacancy on our platform.
Leverage our innovative hiring process





What our clients say about
working with us
You are in good company.
Brian Chen
Director, Web Development, Tessera
Emily Sandler
HR Manager, Near Solutions
Michael Zhang
Director, Talent Acquisition
Susie Davis
HR Manager
Angela Gomez
Senior QA Manager, Alere
David Kim
Senior Project Lead
Nathan Wright
Recruiting Lead, Carestream
Sam Moralez
Senior Program Manager, JDA Soft
Frequently asked questions about hiring engineers
Frequently asked questions
about hiring engineers
To hire software engineers on Sourcer, start by posting your open vacancy with detailed job requirements and desired skills for a software engineer role. Our talent suppliers will submit matching resource profiles of suitable software engineer candidates from their resource pools who are immediately available to join your project team. Review the submissions and shortlist software engineer candidates based on their profiles, skillsets, education, and job experience. Schedule interviews with your top choices for software engineer roles directly through our platform. Finally, select the best candidate for your software engineer vacancy and start the engagement directly on our platform.
The process for hiring software engineers on Sourcer is fast and efficient, thanks to a vast pool of immediately available local and remote software engineer resources available on our platform. You will typically receive software engineer profile submissions from our talent suppliers within 48 hours of posting your software engineer vacancy. Once you have interviewed and selected your preferred software engineer candidates, they can start working almost immediately. The whole process of hiring a software engineer could take as little as two to three days if your team is ready to interview software engineer candidates immediately and can make a hiring decision quickly.
On Sourcer, you can expect to find a wide range of billing rates for software engineers, typically ranging anywhere from $20 to $200 per hour. The exact rate depends on the candidate’s seniority, expertise, and location. This allows you to choose the best fit for your project’s budget and requirements. Your account manager will be able to provide you with additional guidance on prevailing software engineer billing rates for each location type if needed.
The number of software engineer candidates offered for your review on Sourcer depends on the popularity of the skillset, the number of currently available qualified software engineer candidates on our platform, and how long the vacancy remains open in the system. Popular roles and competitive offers typically attract more submissions, giving you a broader selection of software engineer candidates to choose from. On average, you can expect at least 20-30 software engineer candidates to be submitted for your review.
No, not all software engineer candidates on Sourcer are remote. We offer both local and remote candidates to suit your specific project needs. We have software engineer candidates for any location type you may need – onsite, onshore, nearshore and offshore. However, keep in mind that the more restrictive your requirements are, the fewer software engineer candidates you may have to choose from.
You can hire a single software engineer or an entire team of software engineers through Sourcer. It is completely up to you as a client. We can accommodate both options based on your project needs, providing the flexibility to scale your workforce up or down as required. We have thousands of immediately available candidates, including software engineers, on our platform to choose from.
The software engineer candidates offered to you through Sourcer are generally not available or even discoverable by your recruiting team via any other channels. Sourcer offers you more candidates to pick from along with the best billing rates for any software engineer role. Also, unlike other platforms, the candidates we present to you are not freelancers who may end up being unreliable, produce poor quality of work and disappear on you at any moment. Every software engineer candidate offered for your review via our platform has been fully vetted and has their employer backing them to ensure high quality of work, great reliability and full compliance.
Guidelines for
hiring engineers
When it comes to hiring software engineers, understanding the nuances of the role and the process is crucial. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the demand for skilled software engineers is skyrocketing across various industries. Whether you are an HR professional, a recruiter, or a business owner, successfully hiring top talent requires a deep understanding of what the role entails, the necessary skills and qualifications, and the best practices for recruitment. This comprehensive guide answers common questions around hiring software engineers, offering expert insights to streamline your hiring process and ensure you find the best candidates for your team.
What is engineering?
Engineering is an expansive discipline that integrates scientific principles and practical applications to design, build, and maintain structures, machines, devices, systems, and processes. Broadly speaking, engineering is about problem-solving and innovation. Engineers apply mathematical, scientific, and technical knowledge to address real-world problems and create efficient, functional solutions.
Software Engineering
Within the realm of engineering, software engineering focuses explicitly on the design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance of software systems. It adapts engineering methodologies and applies them to create software that is reliable, efficient, and scalable. Software engineers systematically approach problems, leveraging algorithms, data structures, and programming languages to develop software that fulfills specified requirements.
Software engineering can be subdivided into various branches, each specializing in different aspects of software creation:
- System Engineering: Focuses on building foundational software that other applications run on, such as operating systems and server software.
- Application Engineering: Involves creating user-centric applications, like mobile apps, desktop applications, and web services.
- Embedded Software Engineering: Deals with software embedded within hardware devices ranging from consumer electronics to automotive systems.
In summary, while engineering as a whole involves problem-solving across various domains, software engineering zeros in on developing software solutions, meticulously translating user requirements into functional, efficient, and robust software applications.
What does an engineer do?
Software engineers are instrumental in developing the digital infrastructure that modern society relies on. Their roles and responsibilities are multifaceted and cover the entire software development lifecycle.
Here’s a breakdown of what they typically do:
- Requirement Analysis: Understanding and gathering client or stakeholder requirements to determine what the software application should accomplish.
- Design: Crafting architectural blueprints and planning the software’s structure, including defining software elements, data flows, and interfaces.
- Development/Coding: Writing clean, efficient, and maintainable code to implement the software’s functionalities, following best practices and coding standards.
- Testing: Conducting various tests (unit testing, integration testing, system testing) to ensure the software is bug-free, secure, and performs as expected.
- Deployment: Moving the software from a testing environment to a live production environment, ensuring minimal downtime and disruption.
- Maintenance: Ongoing support and updates are necessary to fix bugs, enhance performance, and add new features as user needs evolve.
- Documentation: Creating detailed documentation to guide users and other developers in understanding and using the software.
- Collaboration: Working closely with cross-functional teams, including product managers, designers, and other engineers, to achieve project goals.
Software engineers must juggle technical skills with problem-solving abilities and effective communication to ensure the successful delivery of software projects.
How are engineers usually being used?
Software engineers are a versatile asset to any organization, contributing in various capacities based on the company’s needs and project requirements. Here are some common scenarios:
- Product Development: Engineers are vital in creating new software products tailored to market needs. They work through the entire product lifecycle, from conceptualization to deployment, ensuring the product is both functional and user-friendly.
- Maintenance and Support: Once a product is launched, engineers continue to play a crucial role by providing maintenance and support. This includes troubleshooting issues, releasing updates, and performing regular performance checks to ensure the software runs smoothly.
- Research and Development (R&D): Engineers engaged in R&D focus on innovating new technologies, methodologies, or improving existing ones. They might develop prototypes, conduct experiments, and analyze outcomes to push technological boundaries.
- Quality Assurance (QA): While there are dedicated QA professionals, software engineers are also involved in the QA process. They write and execute tests, and often develop automated testing scripts to ensure the software meets quality standards before release.
- Infrastructure Development: Engineers are responsible for building and maintaining the internal tools and systems that support various business functions. This can include creating continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, managing databases, and developing APIs.
- Consulting and Advisory: Some engineers work as consultants, providing expert advice on best practices for software development, system design, and technology adoption. They help organizations make informed decisions and improve their development processes.
By leveraging the diverse skill sets of software engineers, organizations can drive innovation, maintain high-quality products, and achieve their strategic objectives efficiently.
Required skills and qualifications
Hiring a competent software engineer requires an understanding of essential skills and qualifications. Identifying these can help streamline the recruitment process and ensure you attract top talent.
Technical Skills
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in key programming languages such as Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, or Ruby. The specific language expertise required can vary depending on the project or company.
- Algorithms and Data Structures: Understanding complex algorithms and data structures is crucial as they form the backbone of efficient problem-solving and software design.
- Software Development Methodologies: Familiarity with Agile, Scrum, or DevOps practices can enhance the software development process’s efficiency and collaboration.
- Frameworks and Libraries: Knowledge of popular frameworks and libraries (such as React for JavaScript, Django for Python) that streamline development work.
- Database Management: Proficiency in SQL and NoSQL databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, etc.
- Version Control: Expertise in version control systems (mainly Git) is essential for collaborative development.
- Testing and Debugging: Skills in writing and executing test cases, debugging, and using testing frameworks like JUnit (Java) or PyTest (Python).
Soft Skills
- Communication: Ability to articulate technical jargon to non-technical stakeholders and collaborate effectively within a team.
- Problem-Solving: Strong analytical and troubleshooting skills to diagnose and resolve complex software issues.
- Time Management: Efficiently managing tasks and meeting deadlines in a fast-paced environment.
- Adaptability: Being flexible and open to learning new technologies and methodologies as needed.
Educational Background
- A degree in Computer Science, Software Engineering, or a related field is often a baseline requirement.
- For senior roles, advanced degrees (MS/Ph.D.) or specialized certifications can be advantageous.
Experience
- Previous work experience in software engineering roles, internships, or notable personal projects can provide practical insights and add value to a candidate’s profile.
- Contributions to open-source projects or participation in coding competitions (like Hackathons) can demonstrate dedication and skills.
Popular engineering languages and libraries
Software engineers use a wide range of programming languages and libraries to accomplish various tasks. The choice of language and library often depends on the project’s requirements and the specific domain in which the engineer operates.
JavaScript and its Libraries
- JavaScript: Ubiquitous in web development, it enables dynamic interactivity on websites.
- React: A JavaScript library for building user interfaces, particularly single-page applications. Managed by Facebook.
- Angular: A complete front-end development framework maintained by Google, suitable for building dynamic web applications.
- Vue.js: An approachable JavaScript framework that can be incrementally adopted.
Python and its Libraries
- Python: Known for its simplicity and versatility, Python is popular for web development, data science, scripting, and automation.
- Django: A high-level Python Web framework that simplifies the creation of complex, database-driven websites.
- Flask: A micro-framework for web development in Python that’s easy to get started with.
- TensorFlow & PyTorch: Essential for machine learning and data science applications.
Java and its Libraries
- Java: Predominantly used for building large-scale enterprise applications.
- Spring: A comprehensive framework for enterprise Java development that offers support for various aspects of app development.
- Hibernate: An object-relational mapping (ORM) tool for Java, simplifying database interactions.
C/C++ and its Libraries
- C/C++: Essential for system software and applications requiring high performance.
- Boost: A collection of portable C++ source libraries that significantly facilitate software development.
- Qt: A C++ framework used for developing cross-platform applications.
Ruby and its Libraries
- Ruby: Known for its ease of use and productivity.
- Ruby on Rails: A full-stack web application framework that simplifies the development of robust web applications.
By understanding the landscape of popular languages and libraries, you can better evaluate a candidate’s proficiency and fit for specific projects.
Popular engineering programming tools
The right tools can significantly enhance a software engineer’s productivity and collaboration. Here are some of the most widely used programming tools:
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
- JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA: A feature-rich IDE for Java development that supports a range of other languages.
- Visual Studio Code: A lightweight, open-source editor from Microsoft that supports multiple programming languages through extensions.
- Eclipse: A robust IDE traditionally used for Java development but also supports various other languages through plugins.
Version Control Systems
- Git: An essential tool for version control that allows multiple developers to work on a codebase concurrently.
- GitHub/GitLab: Platforms that host Git repositories and offer additional features like project management and CI/CD pipelines.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Tools
- Jenkins: An open-source tool that automates building, testing, and deploying code.
- Travis CI: A CI service used to build and test software projects hosted on GitHub.
- CircleCI: Enables faster development and ensures code quality by building and testing code with every change.
Project Management Tools
- Jira: A robust tool for tracking and managing software development projects, particularly Agile projects.
- Asana: A flexible project management tool that helps teams manage projects, tasks, and workflows efficiently.
- Trello: A visual tool for managing projects and organizing tasks using boards, lists, and cards.
Testing Frameworks
- JUnit: A testing framework for Java that helps write and run repeatable automated tests.
- PyTest: A framework for Python that allows for simple unit tests and complex functional testing.
- Selenium: Used for automating web applications for testing purposes, ensuring they work as expected across different browsers.
By leveraging these tools, software engineers can boost their efficiency and collaborate more effectively, contributing to the overall success of software development projects.
How much does it cost to hire an engineer?
The cost of hiring a software engineer varies widely based on several factors, including geographic location, experience level, and the complexity of the required skill set. Understanding these factors will help you budget accurately and attract the right talent.
Geographic Location
- United States: Salary expectations can range broadly. In major tech hubs like San Francisco and New York, engineers can command higher salaries, often starting at $100,000 and going up to $160,000 or more for senior roles.
- Europe: Salaries are generally lower than in the U.S., with entry-level positions starting around €45,000-€60,000 in major cities like Berlin or London. Senior roles can go up to €90,000-€120,000.
- Asia: Salaries vary significantly. In countries like India, entry-level positions may start at around ₹400,000-₹700,000 per year, with senior roles reaching ₹2,000,000-₹3,000,000.
Experience Level
- Entry-Level Engineers: Fresh graduates or those with less than two years of experience can expect annual salaries ranging from $50,000 to $70,000 in the U.S.
- Mid-Level Engineers: With around 3-5 years of experience, annual salaries typically range between $70,000 and $100,000.
- Senior Engineers: Those with over five years of experience and specialized expertise can command salaries from $100,000 to $150,000 or more annually.
Skill Set
- Generalists: Engineers with a broad but shallow skill set usually have lower salary expectations compared to specialists.
- Specialists: Engineers specializing in areas like machine learning, blockchain, or cybersecurity often command higher salaries due to the niche skills and experience required.
Freelance and Contract-Based
- Freelancers: Freelancers typically charge on an hourly basis, with rates ranging from $50 to $200 per hour depending on their expertise and market demand.
- Contract-Based: Contract engineers are usually hired for fixed terms or projects, and their pay can vary widely based on the project’s complexity and duration.
By understanding these variables, you can offer competitive salaries that attract top talent while aligning with your budget.
How to find engineers for your team?
Attracting top engineering talent can be competitive. Here are some effective strategies to find engineers:
Job Posting Sites
- LinkedIn: A powerful platform for professional networking and job postings, especially for technical roles.
- Indeed: A broad job search engine that attracts a large audience across various industries.
- Glassdoor: Known for company reviews, it’s also a valuable resource for job postings and employer branding.
Developer Community Sites
- GitHub: Engage with developers by exploring their open-source contributions and repositories.
- Stack Overflow: A platform where developers seek and share technical knowledge. Posting job ads here can attract skilled engineers.
- HackerRank: This platform not only allows you to post jobs but also lets you assess candidates through coding challenges.
University Career Services
- Campus Recruiting: Partner with universities to attend career fairs and engage with students directly.
- Internships: Offer internship programs that can serve as a pipeline for full-time hires.
Recruitment Agencies
- Specialized Tech Agencies: Agencies that focus on tech talent can expedite the hiring process by providing pre-vetted candidates.
- General Recruitment Firms: While less specialized, these firms can still offer valuable assistance in filling roles.
Networking Events
- Tech Meetups: Attend local tech meetups to network with engineers and discuss potential opportunities.
- Hackathons: Sponsoring or participating in hackathons can help you spot and recruit top talent.
- Industry Conferences: Attend conferences to engage with engineers and professionals from around the world.
Employee Referrals
- Internal Programs: Encourage your current employees to refer qualified candidates by offering referral bonuses. Employees often have connections within the industry and can help you find candidates faster.
By leveraging these strategies, you can cast a wide net to attract a diverse range of engineering candidates.
Benefits of hiring engineers on Sourcer
Hiring engineers through Sourcer offers several distinct advantages that can expedite and enhance your recruitment process:
Pre-Vetted Talent
- Quality Assurance: Sourcer connects you with pre-vetted engineers who have been assessed for their skills and experience, reducing the time spent on initial vetting and screening.
- Immediate Availability: Access to a pool of engineers who are ready to start, accelerating your hiring timeline.
Time Efficiency
- Streamlined Process: Sourcer handles much of the legwork associated with recruiting, such as sourcing, screening, and initial interviews, allowing your HR team to focus on final rounds and decision-making.
- Faster Hiring: By connecting with pre-vetted and immediately available candidates, you can significantly reduce the time it takes to fill positions, allowing projects to start sooner.
Scalability
- Flexible Hiring: Sourcer enables you to easily scale your team up or down based on your current project needs. Whether you need more engineers for a large project or fewer for maintenance phases, Sourcer provides the flexibility to adapt quickly.
- Project-Based Hiring: You can hire engineers on a project basis, ensuring you have the right talent for specific tasks without the long-term commitment.
Cost-Effective
- Budget Friendly: Sourcer can help you find the right talent that fits your budget, often at a lower cost than traditional recruitment agencies.
- Reduced Overhead: By handling the recruitment process, Sourcer minimizes administrative overhead and allows your HR team to focus on other critical tasks.
Diverse Talent Pool
- Wide Range of Skills: Access to a wide range of engineers with varied skills, including generalists and specialists, to meet the specific needs of your projects.
- Global Reach: Sourcer’s network includes talent from around the world, giving you access to engineers who might not be available locally.
Enhanced Employer Branding
- Positive Candidate Experience: Sourcer’s streamlined and efficient hiring process ensures a positive experience for candidates, enhancing your reputation as an employer of choice.
- Employer Matching: Sourcer uses advanced matching algorithms to ensure a good fit between the engineer’s skills and your company’s requirements, reducing turnover and improving employee satisfaction.
In summary, hiring engineers through Sourcer can offer significant benefits, from accessing pre-vetted, highly skilled talent to boosting your overall recruitment efficiency. By understanding the essential aspects of hiring software engineers, you can make informed decisions that ensure the successful growth of your engineering team.
Guidelines for
hiring engineers
When it comes to hiring software engineers, understanding the nuances of the role and the process is crucial. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the demand for skilled software engineers is skyrocketing across various industries. Whether you are an HR professional, a recruiter, or a business owner, successfully hiring top talent requires a deep understanding of what the role entails, the necessary skills and qualifications, and the best practices for recruitment. This comprehensive guide answers common questions around hiring software engineers, offering expert insights to streamline your hiring process and ensure you find the best candidates for your team.
What is engineering?
Engineering is an expansive discipline that integrates scientific principles and practical applications to design, build, and maintain structures, machines, devices, systems, and processes. Broadly speaking, engineering is about problem-solving and innovation. Engineers apply mathematical, scientific, and technical knowledge to address real-world problems and create efficient, functional solutions.
Software Engineering
Within the realm of engineering, software engineering focuses explicitly on the design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance of software systems. It adapts engineering methodologies and applies them to create software that is reliable, efficient, and scalable. Software engineers systematically approach problems, leveraging algorithms, data structures, and programming languages to develop software that fulfills specified requirements.
Software engineering can be subdivided into various branches, each specializing in different aspects of software creation:
- System Engineering: Focuses on building foundational software that other applications run on, such as operating systems and server software.
- Application Engineering: Involves creating user-centric applications, like mobile apps, desktop applications, and web services.
- Embedded Software Engineering: Deals with software embedded within hardware devices ranging from consumer electronics to automotive systems.
In summary, while engineering as a whole involves problem-solving across various domains, software engineering zeros in on developing software solutions, meticulously translating user requirements into functional, efficient, and robust software applications.
What does an engineer do?
Software engineers are instrumental in developing the digital infrastructure that modern society relies on. Their roles and responsibilities are multifaceted and cover the entire software development lifecycle.
Here’s a breakdown of what they typically do:
- Requirement Analysis: Understanding and gathering client or stakeholder requirements to determine what the software application should accomplish.
- Design: Crafting architectural blueprints and planning the software’s structure, including defining software elements, data flows, and interfaces.
- Development/Coding: Writing clean, efficient, and maintainable code to implement the software’s functionalities, following best practices and coding standards.
- Testing: Conducting various tests (unit testing, integration testing, system testing) to ensure the software is bug-free, secure, and performs as expected.
- Deployment: Moving the software from a testing environment to a live production environment, ensuring minimal downtime and disruption.
- Maintenance: Ongoing support and updates are necessary to fix bugs, enhance performance, and add new features as user needs evolve.
- Documentation: Creating detailed documentation to guide users and other developers in understanding and using the software.
- Collaboration: Working closely with cross-functional teams, including product managers, designers, and other engineers, to achieve project goals.
Software engineers must juggle technical skills with problem-solving abilities and effective communication to ensure the successful delivery of software projects.
How are engineers usually being used?
Software engineers are a versatile asset to any organization, contributing in various capacities based on the company’s needs and project requirements. Here are some common scenarios:
- Product Development: Engineers are vital in creating new software products tailored to market needs. They work through the entire product lifecycle, from conceptualization to deployment, ensuring the product is both functional and user-friendly.
- Maintenance and Support: Once a product is launched, engineers continue to play a crucial role by providing maintenance and support. This includes troubleshooting issues, releasing updates, and performing regular performance checks to ensure the software runs smoothly.
- Research and Development (R&D): Engineers engaged in R&D focus on innovating new technologies, methodologies, or improving existing ones. They might develop prototypes, conduct experiments, and analyze outcomes to push technological boundaries.
- Quality Assurance (QA): While there are dedicated QA professionals, software engineers are also involved in the QA process. They write and execute tests, and often develop automated testing scripts to ensure the software meets quality standards before release.
- Infrastructure Development: Engineers are responsible for building and maintaining the internal tools and systems that support various business functions. This can include creating continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, managing databases, and developing APIs.
- Consulting and Advisory: Some engineers work as consultants, providing expert advice on best practices for software development, system design, and technology adoption. They help organizations make informed decisions and improve their development processes.
By leveraging the diverse skill sets of software engineers, organizations can drive innovation, maintain high-quality products, and achieve their strategic objectives efficiently.
Required skills and qualifications
Hiring a competent software engineer requires an understanding of essential skills and qualifications. Identifying these can help streamline the recruitment process and ensure you attract top talent.
Technical Skills
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in key programming languages such as Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, or Ruby. The specific language expertise required can vary depending on the project or company.
- Algorithms and Data Structures: Understanding complex algorithms and data structures is crucial as they form the backbone of efficient problem-solving and software design.
- Software Development Methodologies: Familiarity with Agile, Scrum, or DevOps practices can enhance the software development process’s efficiency and collaboration.
- Frameworks and Libraries: Knowledge of popular frameworks and libraries (such as React for JavaScript, Django for Python) that streamline development work.
- Database Management: Proficiency in SQL and NoSQL databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, etc.
- Version Control: Expertise in version control systems (mainly Git) is essential for collaborative development.
- Testing and Debugging: Skills in writing and executing test cases, debugging, and using testing frameworks like JUnit (Java) or PyTest (Python).
Soft Skills
- Communication: Ability to articulate technical jargon to non-technical stakeholders and collaborate effectively within a team.
- Problem-Solving: Strong analytical and troubleshooting skills to diagnose and resolve complex software issues.
- Time Management: Efficiently managing tasks and meeting deadlines in a fast-paced environment.
- Adaptability: Being flexible and open to learning new technologies and methodologies as needed.
Educational Background
- A degree in Computer Science, Software Engineering, or a related field is often a baseline requirement.
- For senior roles, advanced degrees (MS/Ph.D.) or specialized certifications can be advantageous.
Experience
- Previous work experience in software engineering roles, internships, or notable personal projects can provide practical insights and add value to a candidate’s profile.
- Contributions to open-source projects or participation in coding competitions (like Hackathons) can demonstrate dedication and skills.
Popular engineering languages and libraries
Software engineers use a wide range of programming languages and libraries to accomplish various tasks. The choice of language and library often depends on the project’s requirements and the specific domain in which the engineer operates.
JavaScript and its Libraries
- JavaScript: Ubiquitous in web development, it enables dynamic interactivity on websites.
- React: A JavaScript library for building user interfaces, particularly single-page applications. Managed by Facebook.
- Angular: A complete front-end development framework maintained by Google, suitable for building dynamic web applications.
- Vue.js: An approachable JavaScript framework that can be incrementally adopted.
Python and its Libraries
- Python: Known for its simplicity and versatility, Python is popular for web development, data science, scripting, and automation.
- Django: A high-level Python Web framework that simplifies the creation of complex, database-driven websites.
- Flask: A micro-framework for web development in Python that’s easy to get started with.
- TensorFlow & PyTorch: Essential for machine learning and data science applications.
Java and its Libraries
- Java: Predominantly used for building large-scale enterprise applications.
- Spring: A comprehensive framework for enterprise Java development that offers support for various aspects of app development.
- Hibernate: An object-relational mapping (ORM) tool for Java, simplifying database interactions.
C/C++ and its Libraries
- C/C++: Essential for system software and applications requiring high performance.
- Boost: A collection of portable C++ source libraries that significantly facilitate software development.
- Qt: A C++ framework used for developing cross-platform applications.
Ruby and its Libraries
- Ruby: Known for its ease of use and productivity.
- Ruby on Rails: A full-stack web application framework that simplifies the development of robust web applications.
By understanding the landscape of popular languages and libraries, you can better evaluate a candidate’s proficiency and fit for specific projects.
Popular engineering programming tools
The right tools can significantly enhance a software engineer’s productivity and collaboration. Here are some of the most widely used programming tools:
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
- JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA: A feature-rich IDE for Java development that supports a range of other languages.
- Visual Studio Code: A lightweight, open-source editor from Microsoft that supports multiple programming languages through extensions.
- Eclipse: A robust IDE traditionally used for Java development but also supports various other languages through plugins.
Version Control Systems
- Git: An essential tool for version control that allows multiple developers to work on a codebase concurrently.
- GitHub/GitLab: Platforms that host Git repositories and offer additional features like project management and CI/CD pipelines.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Tools
- Jenkins: An open-source tool that automates building, testing, and deploying code.
- Travis CI: A CI service used to build and test software projects hosted on GitHub.
- CircleCI: Enables faster development and ensures code quality by building and testing code with every change.
Project Management Tools
- Jira: A robust tool for tracking and managing software development projects, particularly Agile projects.
- Asana: A flexible project management tool that helps teams manage projects, tasks, and workflows efficiently.
- Trello: A visual tool for managing projects and organizing tasks using boards, lists, and cards.
Testing Frameworks
- JUnit: A testing framework for Java that helps write and run repeatable automated tests.
- PyTest: A framework for Python that allows for simple unit tests and complex functional testing.
- Selenium: Used for automating web applications for testing purposes, ensuring they work as expected across different browsers.
By leveraging these tools, software engineers can boost their efficiency and collaborate more effectively, contributing to the overall success of software development projects.
How much does it cost to hire an engineer?
The cost of hiring a software engineer varies widely based on several factors, including geographic location, experience level, and the complexity of the required skill set. Understanding these factors will help you budget accurately and attract the right talent.
Geographic Location
- United States: Salary expectations can range broadly. In major tech hubs like San Francisco and New York, engineers can command higher salaries, often starting at $100,000 and going up to $160,000 or more for senior roles.
- Europe: Salaries are generally lower than in the U.S., with entry-level positions starting around €45,000-€60,000 in major cities like Berlin or London. Senior roles can go up to €90,000-€120,000.
- Asia: Salaries vary significantly. In countries like India, entry-level positions may start at around ₹400,000-₹700,000 per year, with senior roles reaching ₹2,000,000-₹3,000,000.
Experience Level
- Entry-Level Engineers: Fresh graduates or those with less than two years of experience can expect annual salaries ranging from $50,000 to $70,000 in the U.S.
- Mid-Level Engineers: With around 3-5 years of experience, annual salaries typically range between $70,000 and $100,000.
- Senior Engineers: Those with over five years of experience and specialized expertise can command salaries from $100,000 to $150,000 or more annually.
Skill Set
- Generalists: Engineers with a broad but shallow skill set usually have lower salary expectations compared to specialists.
- Specialists: Engineers specializing in areas like machine learning, blockchain, or cybersecurity often command higher salaries due to the niche skills and experience required.
Freelance and Contract-Based
- Freelancers: Freelancers typically charge on an hourly basis, with rates ranging from $50 to $200 per hour depending on their expertise and market demand.
- Contract-Based: Contract engineers are usually hired for fixed terms or projects, and their pay can vary widely based on the project’s complexity and duration.
By understanding these variables, you can offer competitive salaries that attract top talent while aligning with your budget.
How to find engineers for your team?
Attracting top engineering talent can be competitive. Here are some effective strategies to find engineers:
Job Posting Sites
- LinkedIn: A powerful platform for professional networking and job postings, especially for technical roles.
- Indeed: A broad job search engine that attracts a large audience across various industries.
- Glassdoor: Known for company reviews, it’s also a valuable resource for job postings and employer branding.
Developer Community Sites
- GitHub: Engage with developers by exploring their open-source contributions and repositories.
- Stack Overflow: A platform where developers seek and share technical knowledge. Posting job ads here can attract skilled engineers.
- HackerRank: This platform not only allows you to post jobs but also lets you assess candidates through coding challenges.
University Career Services
- Campus Recruiting: Partner with universities to attend career fairs and engage with students directly.
- Internships: Offer internship programs that can serve as a pipeline for full-time hires.
Recruitment Agencies
- Specialized Tech Agencies: Agencies that focus on tech talent can expedite the hiring process by providing pre-vetted candidates.
- General Recruitment Firms: While less specialized, these firms can still offer valuable assistance in filling roles.
Networking Events
- Tech Meetups: Attend local tech meetups to network with engineers and discuss potential opportunities.
- Hackathons: Sponsoring or participating in hackathons can help you spot and recruit top talent.
- Industry Conferences: Attend conferences to engage with engineers and professionals from around the world.
Employee Referrals
- Internal Programs: Encourage your current employees to refer qualified candidates by offering referral bonuses. Employees often have connections within the industry and can help you find candidates faster.
By leveraging these strategies, you can cast a wide net to attract a diverse range of engineering candidates.
Benefits of hiring engineers on Sourcer
Hiring engineers through Sourcer offers several distinct advantages that can expedite and enhance your recruitment process:
Pre-Vetted Talent
- Quality Assurance: Sourcer connects you with pre-vetted engineers who have been assessed for their skills and experience, reducing the time spent on initial vetting and screening.
- Immediate Availability: Access to a pool of engineers who are ready to start, accelerating your hiring timeline.
Time Efficiency
- Streamlined Process: Sourcer handles much of the legwork associated with recruiting, such as sourcing, screening, and initial interviews, allowing your HR team to focus on final rounds and decision-making.
- Faster Hiring: By connecting with pre-vetted and immediately available candidates, you can significantly reduce the time it takes to fill positions, allowing projects to start sooner.
Scalability
- Flexible Hiring: Sourcer enables you to easily scale your team up or down based on your current project needs. Whether you need more engineers for a large project or fewer for maintenance phases, Sourcer provides the flexibility to adapt quickly.
- Project-Based Hiring: You can hire engineers on a project basis, ensuring you have the right talent for specific tasks without the long-term commitment.
Cost-Effective
- Budget Friendly: Sourcer can help you find the right talent that fits your budget, often at a lower cost than traditional recruitment agencies.
- Reduced Overhead: By handling the recruitment process, Sourcer minimizes administrative overhead and allows your HR team to focus on other critical tasks.
Diverse Talent Pool
- Wide Range of Skills: Access to a wide range of engineers with varied skills, including generalists and specialists, to meet the specific needs of your projects.
- Global Reach: Sourcer’s network includes talent from around the world, giving you access to engineers who might not be available locally.
Enhanced Employer Branding
- Positive Candidate Experience: Sourcer’s streamlined and efficient hiring process ensures a positive experience for candidates, enhancing your reputation as an employer of choice.
- Employer Matching: Sourcer uses advanced matching algorithms to ensure a good fit between the engineer’s skills and your company’s requirements, reducing turnover and improving employee satisfaction.
In summary, hiring engineers through Sourcer can offer significant benefits, from accessing pre-vetted, highly skilled talent to boosting your overall recruitment efficiency. By understanding the essential aspects of hiring software engineers, you can make informed decisions that ensure the successful growth of your engineering team.
Discover talent on our platform
Discover talent on our
platform
| App Store Developers App Product Managers Mobile Project Managers Android Developers C# Developers iOS Developers Mobile UX Designers Mobile UI Designers | Mobile App Designers Mobile Game Designers Flutter Developers Kotlin Developers Xamarin Developers React Native Developers Swift Developers Mobile App Testers |
| Web Designers UI/UX Designers Web Developers Angular Developers JavaScript Developers CSS Developers Web Scraping Developers PHP Developers Backbone.js Developers Vue.js Developers Laravel Developers RxJS Developers | Meteor Developers CodeIgniter Developers CakePHP Developers MEAN Stack Developers Node.js Developers Ruby on Rails Developers API Developers TypeScript Developers Django Developers Yii Developers ASP.NET Developers React.js Developers |
| PyQt Developers DevExpress Developers Qt Developers |
.NET Core Developers .NET Developers Windows Developers |
| Ethereum Developers Smart Contract Developers Blockchain Developers Ethereum Smart Contract Developers |
Hyperledger Developers Cryptocurrency Developers Solidity Developers Distributed Systems Engineers |
| Game Developers Augmented Reality Designers 3D Animators Virtual Reality Developers Augmented Reality Developers Mobile Game Designers Computer Vision Developers iOS Developers |
Android App Developers 2D Animators Digital Artists Unity or Unity3D Developers Three.js Developers Unreal Engine Developers C++ Developers Game Testers |
| LinkedIn API Developers Facebook API Developers API Development Specialists |
Shopify API Developers Stripe Developers Zapier API Developers |
| Firmware Engineers Hardware Engineers Embedded System Developers Electrical Engineers Computer Network Engineers |
IoT Engineers IoT Security Engineers IoT Embedded Engineers IoT Platform Developers IoT Architects |
| Technical Support Engineers IT Support Engineers System Administrators Network Administrators |
Site Reliability Engineers AWS Experts GCP Experts Azure Experts |
| Business Analysts Business Intelligence Analysts Logistics Analysts Statisticians |
Program Analysts Operations Researchers Quantitative Analysts Analytics Engineers |
| C++ Developers Python Developers JavaScript Developers Ruby Developers PHP Developers C Developers Java Developers Rust Developers Erlang Developers |
Clojure Developers Haskell Developers Dart Developers VB.NET Developers Swift Developers Golang Developers Visual Basic Developers Elixir Developers Scala Developers |
| QA Testers Manual Testers QA Leads Selenium Developers |
Test Automation Engineers Jenkins Developers Appium Developers Cucumber Developers |
| DevOps Engineers Data Engineers Database Developers AWS Developers |
Distributed Systems Engineers Docker Developers Kubernetes Developers Azure Developers |
| Data Scientists Machine Learning Engineers Data Engineers Data Analysts Computer Vision Developers Microsoft Access Developers Algorithm Developers MATLAB Developers Power BI Developers |
OpenAI Developers Crystal Reports Developers GPT-3 Developers Hadoop Developers Tableau Developers Python Developers Excel Experts Elasticsearch Developers Chatbot Developers |
| E-commerce Developers WooCommerce Developers Shopify API Developers Magento Developers OpenCart Developers Shopify Developers Salesforce Commerce Cloud Devs | Salesforce Developers Stripe Developers Odoo Developers Google AdWords Developers BigCommerce Developers Hubspot Developers Digital Commerce Testers |
| CMS Developers WordPress Designers WordPress Developers SharePoint Developers |
Drupal Developers Joomla Developers Elementor Developers Webflow Designers |
| UI Designers UX Designers Web Designers Mobile Designers Product Designers | Creative Directors Figma Experts Augmented Reality Designers Sketch Experts UX Researchers |
| Brand Designers Graphic Designers Visual Designers Marketing Designers Logo Designers | Presentation Designers Illustrators Photoshop Experts Creative Designers Motion Graphics Designers |
| Big Data Architects Database Developers MongoDB Developers |
PostgreSQL Developers Oracle SQL Developers Apache Airflow Developers |
| Product Management Consultants Remote Product Managers Technical Product Managers Digital Product Managers |
Technical Project Managers Project Coordinators App Product Managers Web Project Managers |
| Front-end Developers Software Developers Back-end Developers Product Consultants Full-stack Developers Technical Writers Software Architects | Coders Remote Developers Startup Developers Prototype Developers Outsourced Developers Offshore Developers Software Engineers |